Due date: Wednesday, September 24, 2025.
Download the following Python program implementing a simple expert
system:
expert.py
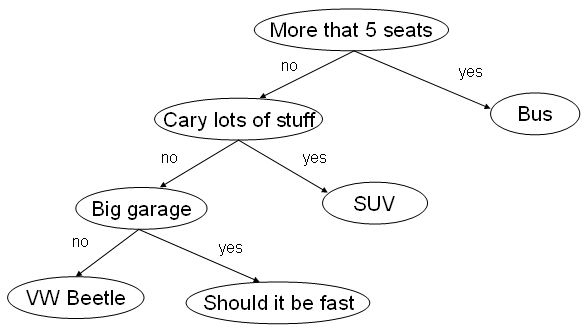
This implements an expert system illustrated in the following
figure:

The idea is to organize the system into a tree. Each internal (non-leaf) node contains a question where the answer is yes or no. Each answer leads to another subtree. The leaf nodes (no children) are terminal nodes where an answer can be given to the user. The system keeps asking the user questions and keeps following the links in the tree until a terminal node is reached and a recommendation can be given.
a. Choose a topic for the expert system such as, choosing a car, choosing food for dinner, fashion advice, choosing a book to read or movie to watch.
In the expert program, change the text of the introduction to reflect the topic of your expert system.
b. Add a function read_db(filename) that reads the expert database from a file and returns a dictionary containing the states and associated information. The function should take a filename as a parameter, assumed to be a string. For simplicity, we'll assume that there are no errors in the file and that the first state the file starts from is always called "initial".
We'll assume that every state is a single word (no spaces) followed by the question to be asked when that state is reached on one line and by the states to move to in case of positive and negative answers on another line together. If the state is terminal, then we'll have an empty line in place of the line containing these two states.
So, we can assume that the file will contain one or more of the following:
state_name Question state_yes state_no
The file car_db.txt contains an example of such a file for the database in the figure above.
The database returned by the function is a Python dictionary where the keys are the states (so they must be unique in your file). The values entered for them are Python lists containing 1 or 3 elements. Terminal nodes will have a list with a single element associated with them where the element is the string displayed for the user for these states. Internal states will have 3 elements in the list: the question to ask the user in that state, the state to go to in case the answer is yes, and the state to go to in case of no. All of these are strings. You can check the function make_car_db for an example.
c. Create your own database file for the expert system containing states and questions in the format described above. Note that the tree doesn't have to be a literal tree, meaning that it's possible to reuse states as reachable from the answers to different questions.
Add at least 10 nodes to the file text. Make sure that any non-terminal state has two children for the two possible answers.
d. Change the test to ask the user for the name of a database file to use. Input this as a string and call the function read_db to input this and store the result in the variable db instead of calling make_car_db. The line calling the expert system function can stay the same.
Create a meme-like image with a text to image AI. Start with a sentence you want to illustrate, like a joke or an ironic statement, an encouraging statement, or a reflection on life or current events. Think of at least two objects that could help illustrate this concept.
Use a text to image AI to create an image corresponding to this text. Add the text over it using any image editor. Here are some systems you can use, or others you may know:
Submit the modified program to Canvas, Homework 4, along with the text file containing the database and the image file for exercise 2. I will create a folder in Canvas where I will upload the image submissions so you can see what other students have created.