
Resolution: pixel density.
Digital image : a matrix of pixels.
Pixel: picture element, unit for screen and digital images.
![]()

Resolution: pixel density.
Screen: 1024x768Pixel encoding:
Printer 300 dpi (dots per inch)
Picture: 76 dpi
B/W: 1 bit/pixelHuman vision: RGB cells (cornets)
16 colors: 4 bits/pixel
256 colors or grays : 8 bits/pixel
True color : 32 bits/pixel
Electromagnetic spectrum: radio, TV, phones, radar, microwave, infrared (heat), visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, Gamma-rays.
Light properties:
electromagnetic waveColor: hue, tone, shade, tint.
frequency (f) and wavelength (l) : c=fl
white light: contains all visible frequencies
red frequency < violet frequency
energy : white energy Ew and dominant energy Ed
Color composition
Primary colors: can produce the others from them
mixing : red, yellow, blue (painting)Complementary colors:
composing : red, green, blue (vision, computer screen)
mixing : red - green, blue - orange, yellow - violet
composing : red - cyan, green - magenta, blue - yellow
TV / screen: matrix of RGB dots.
Printer : matrix of CMY + Black dots.
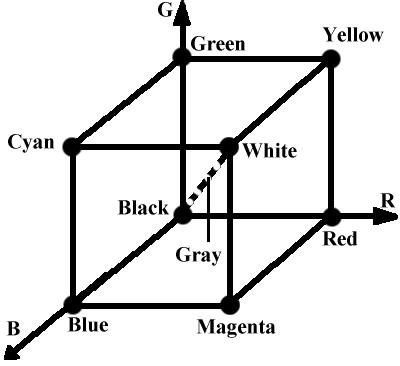
RGB: red, green, blue
[0, 1] [0, 1] [0, 1] or [0, 255] [0, 255] [0, 255]
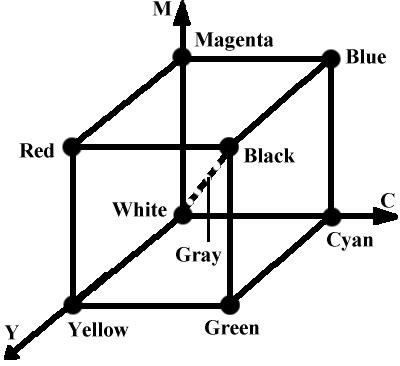
CMY: cyan, magenta, yellow printing
[0, 1] [0, 1] [0, 1]
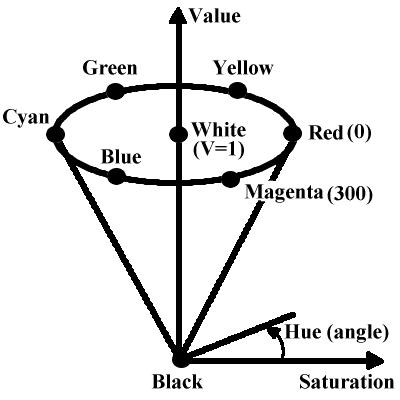
HSV: hue, saturation, value painting programs
[0, 359] [0, 1] [0, 1]
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
(C, M, Y) = (1, 1, 1) - (R, G, B)
HSV
set of primitives like lines, rectangles, spheres, etc., given by coordinatesBitmap:
xfig, ClarisDraw, etc.
high level of compression, easy editing
shape restrictions
set of individual pixelsImages formats:
direct RGB / lookup table or color map
true color / 256 colors or grayscale
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) 256
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) true
BMP (Windows bitmap) 2-true
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) true
TGA (Targa File, SUN) true
PNG (Portable Network Graphics) 256
EPS (Encapsulated PostScript) true
format identificationImage data
image size
image type
image data format
compression type
color map
pixel data (raster)
Graphic Scene and Components