C481 B581 Computer Graphics
Dana Vrajitoru
Shadow, Reflection and Refraction
Global illumination models where objects interact with each other.
All the algorithms in this category take a lot of computational time,
which is proportional to the quality of the resulting image.
Shadow
|
|
|
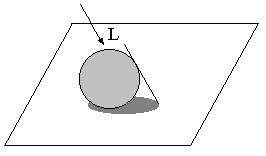
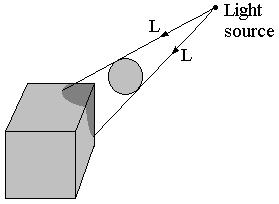
Directional light
|
Point light source
|
Shadow algorithms
Similar to hidden surface algorithms, but considering two projections:
from the viewer's POV and from POV of the light source.
Shadow buffer: the extension of the z-buffer.
-
1 z-buffer for the view plane;
-
1 buffer for each light source;
-
for each point, add the light component of each light source if the point
is visible in the shadow buffer of that light source.
Reflection
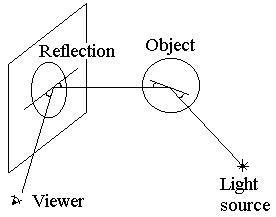
Refraction
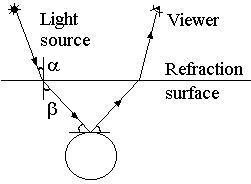
| sin a |
|
n2 |
| ----- |
= |
---- |
| sin b |
|
n1 |
where n1 and n2
are the refraction indexes of the media above and below the refraction
surface.
Shadow in OpenGL
Example: shadow.c
The idea is to duplicate each polygon by applying to it a transformation
based on the position of the light.
The shadow polygon has different light properties, for example, being
much darker than the rest of the scene.

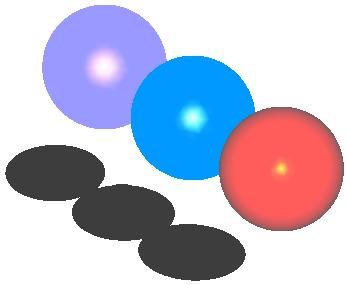
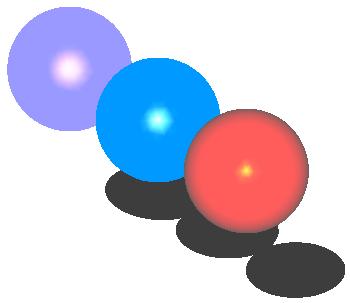
A variation of the spheres program with shadow: sphere_shadow.cc.
Snapshots from this program: